 |
| About The largest Bat In Africa (source) |
About The largest Bat In Africa. Bats are one of the names of mammals which are famous for their ability to fly. Because bats consist of various types, bats also have various sizes. In Africa there, the title of the largest bat on the local continent is held by the Hammer-headed Bat.
About The largest Bat In Africa
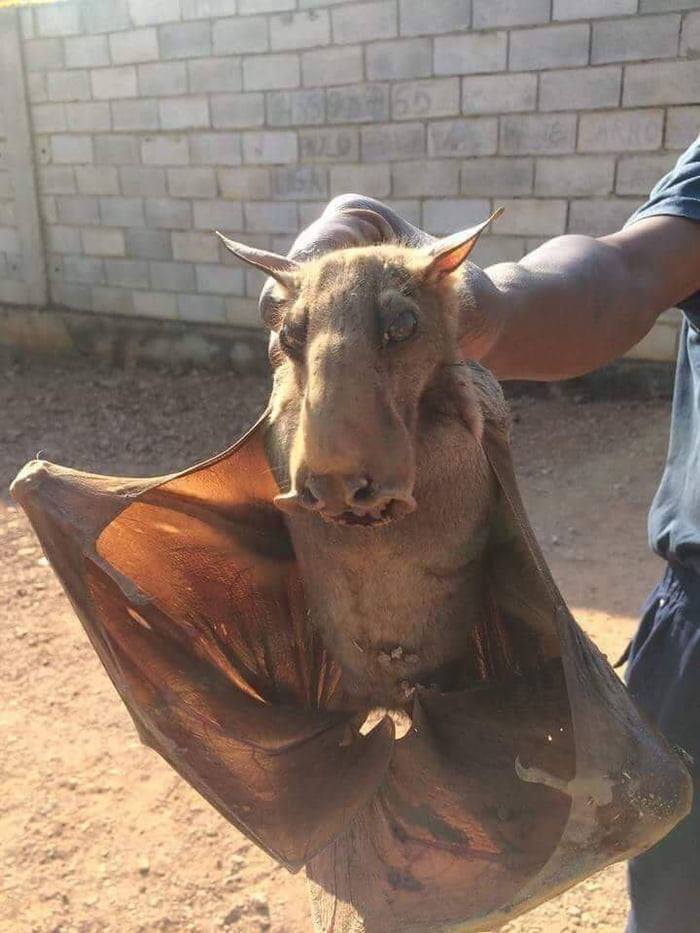
The Hammer-headed Bat or in scientific language Hypsignathus monstrosus is the name of one type of bat that got this name because of its long and large head shape like a hammer. Only male bats have a head like that. The female bat, on the other hand, has a smaller snout.
The unique shape of the Hammer-headed Bat gave rise to speculation about this animal as the true identity of the Jersey Devil, a mysterious creature or cryptid who first appeared in New Jersey, eastern US, in the 18th century.
The Jersey Devil is said to have the appearance of a winged horse that can stand upright. According to one theory, the Jersey Devil may have originally been a Hammer-headed Bat that was kept by the locals, but later escaped from its cage.
This theory is not accepted by some because Hammer-headed Bats are not the size of the Jersey Devil. Then if the Jersey Devil is said to be able to stand upright on two legs like a bird, then the Hammer-headed Bat does not have that ability.
Not a few also thought that the so-called Jersey Devil was originally just a fairy tale made by the local community at that time.
 |
| About The largest Bat In Africa |
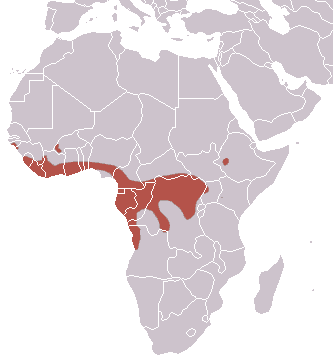
Back to the Hammer-headed Bat problem. The original habitat of the Hammer-headed Bat is on the African continent, precisely on the west coast of Africa and the area around the equator.
They can be found from Senegal to the west, Congo to the east, and Angola to the south. Their favorite habitat is forest areas around rivers and beaches with a maximum elevation of 1,800 meters above sea level.
 |
| About The largest Bat In Africa |
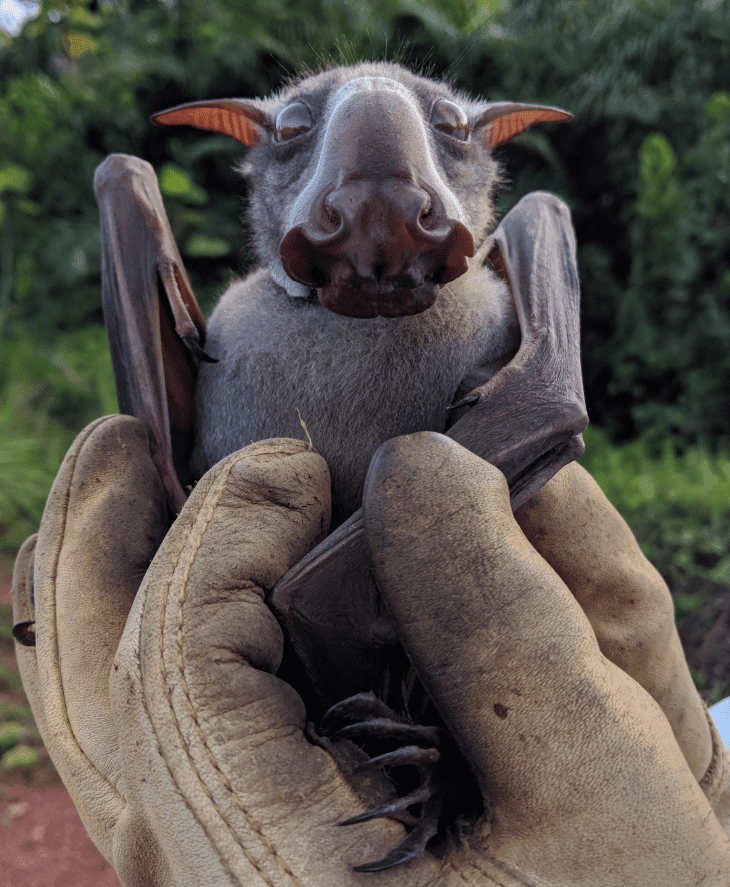
Hammer-headed Bats have a maximum body length of 25 centimeters with a maximum wingspan of nearly 1 meter and an average weight of 377 grams. Its size makes this bat the largest bat species on the African continent.
Male Hammer-headed Bats are generally larger than females. Male Hammer-headed Bats also have a habit of flying farther than females when looking for food.
Very Noisy Dark Beast
Like bats in general, Hammer-headed Bats are nocturnal animals that are active at night. During the day, these bats sleep on tree branches upside down.
Apart from avoiding predators such as eagles, another reason why Hammer-headed Bats are active at night is that they generate large amounts of heat every time they fly.
By flying at night, these bats can keep their body temperature so they don't get too hot. Hammer-headed Bats are fruit eaters.
The types of fruit he consumes include mangoes, bananas and guava. Hammer-headed Bats have also reportedly attacked chickens to eat their flesh and blood.
Big Bat Videos
However, it is not known whether these bats actually have an omnivorous diet because the only source of information that these bats also attack chickens comes from the Van Deusen report in 1968. Meanwhile, there have been no reports of new testimony of this. bats do eat chicken.
To attract female bats, each male bat will make loud noises while still perched and flapping its wings. The male bat's ability to make a loud sound is supported by a large and unique head shape.
If the female is attracted to the male's singing, the female will perch beside the male and then mate with him.
 |
| About The largest Bat In Africa |
The time it takes for male and female bats to have sex is about a minute or less. After that, the female will then immediately leave the male to continue foraging activities.
Hammer-headed Bats are polygynous, which means that a male can mate with several females at once. Males with high rates of successful mating tend to group in the same place.
It is not known what period of pregnancy the female Hammer-headed Bat has. What is commonly known is that normal women will only have one baby per pregnancy.
After birth, female bat babies will suck the mother's milk until a certain age. Only female are involved in childcare activities until they become independent.
Female and male bats experience different growth rates. If female bats have experienced sexual maturity at the age of seven months, then the male bats will experience sexual maturity at the age of one year or more. In the wild, Hammer-headed Bats are known to live up to 30 years.
About Bats And Ebola Disease
Due to its large size, the size of a bat, this Hammer-headed Bat is widely hunted by local residents who are interested in eating its meat.
Although widely hunted, these bats are thought to still have an abundant population and are not yet categorized as endangered animals.
On the other hand, the Hammer-headed Bat is considered an intermediate animal for the Ebola virus, a dangerous disease that can cause its victim to bleed profusely and then die within days.
As many as Tens of thousands of people in West Africa have reportedly died as a result of being infected with Ebola. Apart from attacking humans, Ebola also attacks various types of mammals such as bats, chimpanzees, gorillas and deer.
The Ebola virus that initially infected bats is thought to spread to other species when feces and fruit pieces that have been bitten by bats are touched or eaten by other animals, for example by gorillas.
When an infected gorilla is touched by a human, that human will also catch Ebola. An infected person can infect other people who are still healthy through contact through bodily fluids and sexual intercourse.
Hammer-headed Bats are known to be infected with the Ebola virus because scientists have found antibodies and component fragments of the Ebola virus in the bats' bodies.
However, this virus is known to not make bats sick and only uses bats as a transit point before spreading to other species.
By studying the characteristics of the Ebola virus in bats, scientists hope that the cycle of Ebola spread can be better understood so that future Ebola outbreaks can be avoided.
By: Ochie














0 comments